Osteoarthritis of the Knee: How can Physical Therapy Help?
Osteoarthritis is a “wear-and-tear” disease that affects the joints, and is one of the more common chronic degenerative conditions. As osteoarthritis progresses, the cartilage cushion between joints wears down leading to stiffness, pain, and swelling.
33% of adults aged older than 60 years are affected by osteoarthritis of the knee, making knee pain a common complaint in physical therapy.
Knee osteoarthritis can limit the ability to rise from a chair, stand comfortably, walk, and use stairs.
What are the common treatment options for knee osteoarthritis?
Non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen are pain relief medications commonly used to treat osteoarthritis. Like many pharmaceutical treatments, NSAIDs come with side effects and increased risk of
complications or side effects.
Cortisone injections are another steroidal, localized anti-inflammatory pain relief treatment available. Injections can offer temporary relief especially to help patients return to normal activities. However, injections are not a viable long term treatment, and repeated injections can have detrimental effects.
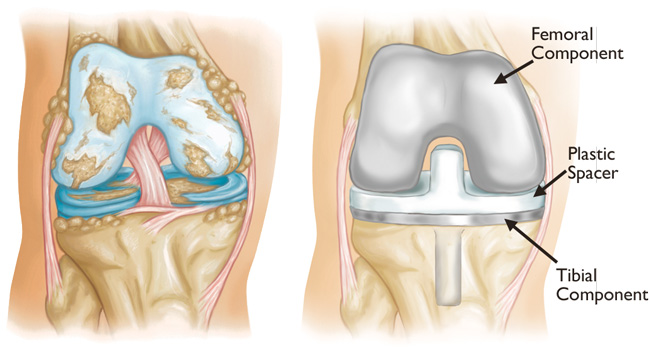
Joint replacement surgery is the final option for knee osteoarthritis, in which the cushioning connective tissue comprising the knee joint is surgically replaced. Surgical treatments inherently carry greater risks for the patient, and require rehabilitation for several months after the procedure.
What does the evidence say about physical therapy and knee osteoarthritis?
Physical therapy consisting of manual therapy combined with range of motion exercises, strengthening and cardiovascular exercise reduces pain and improves function in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Research has demonstrated that patients with knee osteoarthritis who received manual therapy combined with supervised exercise reported a 20-40% relief of symptoms after only 2-3 treatments (Deyle et al, 2000).
Physical therapy is a safe, conservative, and effective treatment